An abandoned mine in Finland is set to be transformed into a giant battery to store renewable energy during periods of excess production.
The Pyhäsalmi Mine, roughly 450 kilometres north of Helsinki, is Europe’s deepest zinc and copper mine and holds the potential to store up to 2 MW of energy within its 1,400-metre-deep shafts.
The disused mine will be fitted with a gravity battery, which uses excess energy from renewable sources like solar and wind in order to lift a heavy weight. During periods of low production, the weight is released and used to power a turbine as it drops.
holds the potential to store up to 2 MW of energy
2nd paragraph and he’s already lost me. It would be nice if tech columnists had the equivalent of even a single semester of high school physics.
I googled
Pyhäsalmi Mine gravitricity "2 MW"and EVERY article covering this has also cited 2 MW.Now, under Occam’s Razor, what’s more likely:
- Absolutely none of the article writers have any clue what the difference between a MW and a MWh is because none of them remember any physics
- Some of them could suspect that it’s wrong, but an authoritative source of the claim wrote/said 2 MW capacity when they meant “2 MW peak generation” or “2 MWh storage” (I’d presume Gravitricity, but I’m struggling to find such a source, myself)
- One writer miswrote/misquoted as per 2, and everyone is mindlessly recycling that original article’s contents with no attribution or care.
I don’t know which one it is. But I’d generally lean against 1.
#2 is certainly food for thought. So the idea is that from a journalistic fact-checking point of view, it is more important to convey the information exactly as it was presented than to verify its accuracy?
This would explain why science/engineering-based articles are so commonly inaccurate or missing in critical details. The journalist can fall back on saying “I have a recording of an interview with the expert after we downed a few pints at the pub, and I’m just parroting back what he said. Don’t shoot the messenger!”
I’d honestly prefer raw parroting in most cases, even if it’s “obviously” wrong. I don’t want people selectively interpreting the facts as have been conveyed to them, unless they’re prepared to do a proper peer review.
That’s what [sic] is for though. You fact check, and then leave the quote as the press release had it.
The problem is that most of these articles are basically reprinting of the press release without any editorial additions at all.
Just FYI, you need an escape backslant (\) preceeding the octothorpe (#) to not have your entire first paragraph bolded.
TIL that # is called an “octothorpe”. Thank you kind stranger.
Then there’s the issue between scientific jargon that is different from general public use. A scientific theory has a specific definition, but it’s easy for general population to dismiss them as “just a theory”.
Or is all just LLMs summarising the same badly translated source.
Mistakes like this could be avoided if we just used joules for energy and watts for power.
Or just joules per second for power. Eliminate watts entirely. Dumbass unit
Well, Watts are just a different way to write Joules per second. The unit we should eliminate is {k,M}W.h which introduce a 3.6 factor in conversions to/from the regular unit system
My fave has gotta be kwh/yr/ft². I came across that while researching the lighting requirements for hydroponics.
These cursed time units remind me of the super messy imperial units. Unfortunately, the French revolution wasn’t able to fix that, but it did fix a whole lot of other nonsense.
Yeah but if we all wrote “joules per second” instead of watts we’d encourage everyone to measure energy in joules instead of watt-hours. It’s like speed, we don’t need an entirely separate unit that just means m/s
Like Mach 1 and Mach 2?
How many horsepower is your car’s gas tank?
Jiggawatts
Jay-z’s preferred unit of energy
That’s a miniscule amount compared to PSH facilities, whether it’s 2 MW capacity or 2 MWh storage.
It’s a cool concept but practically seems limited to niche applications due to the small capacity. Granted it is a prototype, but it also seems intuitive that pumping large amounts of water would be more efficient than moving solid blocks of heavy material for a gravity battery design.
My guess is that that number is simply completely wrong. Bo one would brag about a 2 MW generator or a 2 MWh grid storage.
The thing is, moving a rock up does not need a huge reservoir. You would only (more or less) need the vertical space
I was thinking that you would need increasingly beefy motors and cables/cranes as the size of the rocks scales. But for a reservoir, you could use the same pump over a longer period of time to store much more energy. It’s also easy to utilize a body of water with a volume much greater than the volume of a vertical cylinder.
They were actually planning pumped storage there earlier, with a claimed capacity of 530MWh https://yle.fi/a/3-12593341
deleted by creator
Alright, I’ve been to high school but never understood “Wh”. For speed we say “They are moving at
25 km/haka 25km per hour” --> in one hour the object will have traveled 25km. per indicates division. Same for flow rate (cubic meters per second --> l/s) --> “The swimming pool of 5m³ was filled at0.5m³/hand took 10h to fill”.If something generates or consumes 10W per hour, shouldn’t that be 10W/h not 10Wh? If I hold an object that weighs 100g for an hour, doesn’t that mean I have been exerting myself at the gravitational force of the 100g object for 1 hour -->
(100g * 9.832m²/s) / h-->(100g*9.832m²/s) / 3600sand thus the units beingg * m² * s⁻²which are joules? How does that equate to “watt hours” Can somebody explain this to me conceptually? It makes no sense to me.
2MW is a measure of power, not energy.
Time for something to free fall 1.4km is about 17s, so the minimum capacity is 34MJ or 9.4kWh in order to make their statements true. $1.50 in electricity.
The weight doesn’t have to “free fall” for this to work. It could be a huge boulder that’s lifted a few centimeters per hour. And then it can be dropped a few centimeters per hour when needed.
Run the numbers.
How heavy a boulder? 10,000kg?
Potential energy is mass x height, so 10,000kg x 1,400m which is 14MJ of energy. Sounds like a lot, right?
One Joule is a watt flowing for a second and 1,000 watts flowing for 3,600 seconds is 1kWh. 3,600,000 Joules or 3.6MJ. So our 10 ton rock up a 1.4km shaft only stores 4kWhs? 60¢ of electricity?
Everything is linear here, so even having a 100 ton rock will only get us to half a EV battery.
Edit: if you’re wondering where the other 90 cents went, this example won’t produce two megawatts. It would only produce about 700 kilowatts.
How something be turning a huge ass generator (most likely) AND be in free fall…
You put a rope on it. The rope goes around the generator shaft/alternator as it would be with a steam/wind turbine.
Then it’s not free-fall…
It will be similar to a big pulley.
The weight will pull the turbine, the turbine will require a torque to generate current. This torque will act as an upwards force against gravity. This force will slow the fall of the weight significantly. The turbine ‘consuming’ the torque allows the weight to fall.
The higher the power output the faster it will fall. This will be adjustable. No power out = stationery. A small amount of power out, the descent speed will be tiny. A faster fall a higher power output.
This won’t be designed to fall at full speed. It’ll be designed for a long slow descent. The theoretical power will likely be much higher. It will be limited by the turbine and wiring capacity that’s rated at 2MW.
If your calculations are correct it will be able to generate $1.50 a second. It will also consume power that is below market price/free/paid to consume when it ‘charges’. It also provides the utility of stabilising the electrical grid against renewables. Increasing the capability of the grid to support more cheap renewable energy, without the lead time of nuclear or the pollution of biofuel.
I sincerely doubt this is accurate or why would they even bother.
All solid weight gravity batteries are a scam. The sound good enough to get grant money, but if you run the numbers, they are pitiful batteries.
To make it worth while you need literal lakes of water.
Interesting. Earlier they were planning pumped storage there, with a claimed capacity of 530MWh https://yle.fi/a/3-12593341 Seems like that fell through https://www.epv.fi/en/project/a-pump-storage-station-for-pyhasalmi-mine/
Every source I can find says “2MW” of capacity. I assume they meant 2MWh, though that doesn’t sound like that much.
They’re planning to use the 530 m long secondary shaft at first. The entire mine is a lot deeper, so obviously, there are other shafts too. You gotta start somewhere.
2MW of energy 🤦♂️
Just walked the distance of 1.8 km/h.
I just waited for 2 light-years at the doctor’s office.
Very interesting, and good to hear.
Though, I’m not sure why they would drive a turbine to drive a generator, instead of just driving the generator directly. Their illustration doesn’t show any turbines either.
The illustration also showed a bucket wheel excavator. Don’t remember seeing that the last time I visited Pyhäsalmi.
Just guessing here but I think they are playing with gear ratios. A large turbine with high resistance being slowly turned by a heavy weight could generate power for an extended period of time.
EDIT: Maybe the shaft is the turbine. Like a big rotating corkscrew.
The turbine is the part that turns potential energy into rotational energy. The generator turns that rotation into electricity.
But isn’t the definition of a turbine “a type of machine through which liquid or gas flows and turns a special wheel with blades in order to produce power” with the “power” (aka. rotational energy) going to a generator?
Where does the liquid or gas come from? Isn’t this battery supposed to lift heavy, solid objects?
It doesn’t outright state that it uses solid weights, but their illustration looks more like they’d use a lift with sand or weights, and not a turbine with liquid or steam:
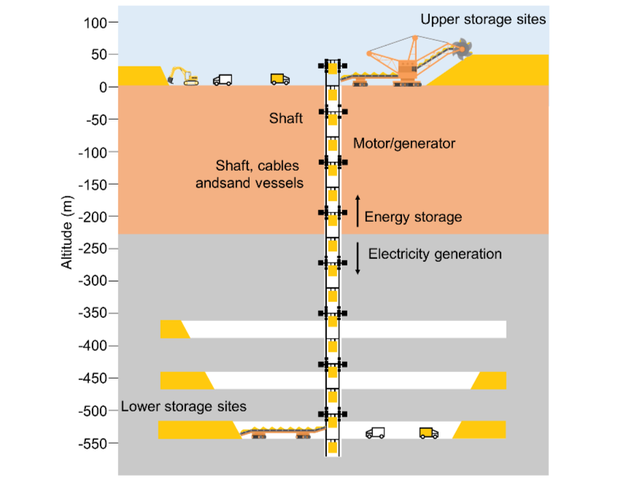
I wasn’t suggesting that a turbine could be used (directly) for sand, I hope you didn’t get that impression, I was just trying to address that commenter’s point of confusion about generators and turbines.
To your question, a flow is cause by a difference in energy potentials between two connected points in a system; Potential energy causes the gas or liquid to flow through a turbine. The more potential energy, the higher the speed, or pressure (depending). Also, not all turbines drive generators. The output could drive anything where you need rotational input, including a vehicle’s transmission. For a lot of reasons, that isn’t usually done.
If I understand correctly, the idea is to store something heavy up top, send it down below using the weight of the sand to somehow (unspecified?) generate electricity, then send it back up when there is an excess supply of energy generation, leaving it available to use again when energy production is reduced. Battery really describes this system better than generator, because it’s only a hole in which to dump excess energy and then pull it out (which, in a roundabout turn of events, the “hole” in this instance is above ground, and then you “pull it out” of the hole by sending it back down.).
All that said, this seems like a boondoggle. I think there’s a lot in this press release that is unsatisfactory, and I’m extremely skeptical that this makes good sense until I see definitive independent proof otherwise.
I’m going to preface this by saying, all I know is that know about the subject was one physics class in college… The teacher mentioned Hydro Pump Storage that pumps water into a reservoir when there is an excess of energy generation then releases it through turbines when there is a surge is energy needs on the grid. Wouldn’t this idea work in a very similar way? If so it would seem feasible as about 15% of the UKs STOR requirements are met in this way.
Yeah, I was imagining it would probably work better with water instead. Sand can’t be pumped (or turbined lol), and I noticed those many enormous trucks carting the sand around underground which seems to introduce an enormous efficiency loss to the system. Good to see the fundamental concept works well in practice, thank you.
That’s so cool!
This is one of those ideas that in hindsight seem so simple and obvious that it makes one wonder how nobody thought of it prior. Absolutely brilliant.
Because it’s super inefficient
Not if the energy would go to waste. This is a mechanical battery to store surplus power generation from things like wind and solar.
They have done this before, only instead of using a big weight, they use water. Lookup “Dinorwig Power Station” for a good example.
That’s similar but different in a lot of meaningful ways. Hydro pumping like that requires a relatively large body of water next to a large geographical height right nearby. This new system doesn’t require any water, and it uses a man made hole in the ground that’s already been created and which otherwise would be simply unused
It’s what we call a double whammy. Paid to remove the metals and then paid for the hole you’ve made.
Sounds like a double win, not a double whammy
Oh interesting, I can see how whammy could be considered negative, but I’ve always heard it used in a positive way.
Huh, definitionally it’s always a bad thing, i wonder why people around you use it that way
Isn’t this a little goofy? It presumes there will be extra electricity. Do you see any sign that we’ll be producing significantly more than we need? All i see is stupid decision after stupid decision. Can’t even build a nuclear reactor these days so barring a fusion breakthrough there are no big leaps to be made. That said, fusion does appear to be coming, but that’d also make this moot and hence silly.
On-demand (or surge) power generation like this is much different then base power generation like you get from solar, wind or nuclear (or theoretically fusion).
Long story short, any functional power grid needs both because generation has to match demand, and demand is uneven and wonky.
The most common surge power source is small natural gas plants. This is a replacement for those.
It presumes there will be extra electricity.
There’s always extra electricity. Eg. Solar generates power during the day, charges this “battery” and then powers lighting at night when demand is higher and people need to be able to see.
There’s always extra electricity. Eg. Solar generates power during the day, charges this “battery” and then powers lighting at night when demand is higher and people need to be able to see.
And this is only set to become more of an issue. Solar and wind are going to be a larger share of the energy mix, but they will still be unreliable. Energy storage, whether physical or chemical, will need to be part of the solution.











