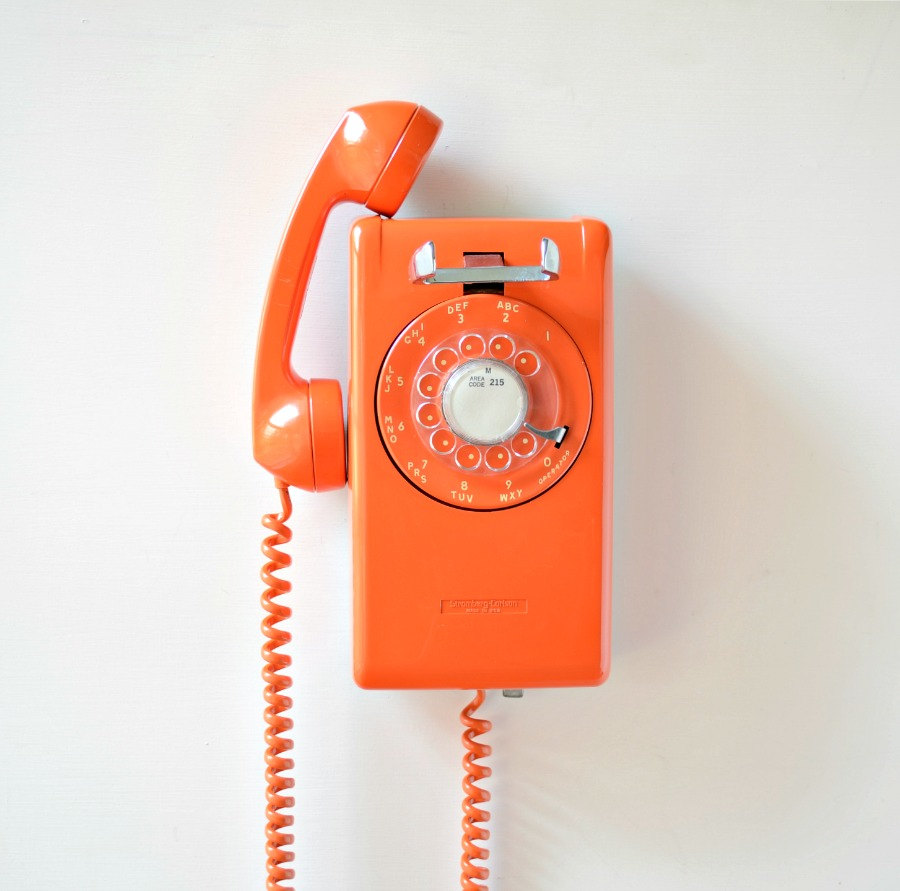
TL;DR This is a drop of the solvent from pen ink dissolving into water and filmed at 1500fps, played back at 30fps, the field of view is 5-7mm ish.
Phenoxyethanol is the solvent in ball point pens that gives the ink it’s distinct smell. It is just barely soluble in water and saturates at a very low concentration, it is more dense than water but small droplets will float unless the water is already saturated. It also has a significantly lower surface tension than water.
On first contact with water the droplet of phenoxyethanol spreads out and is supported on the surface. Soon after the edge of the droplet starts to split into dendrites that wave violently and send out extremely high speed ripples across the water. As the droplet shrinks and breaks up smaller arms form on the larger ones until the droplet wiggles itself into non-existence. What the hell is going on?
When the droplet first contacts the water it begins to dissolve and immediately saturates the area directly below the drop, at the edges of the drop the saturated solution is pulled away by the surface tension gradient around the drop. This gradient sets up a flow of unsaturated water up from below the drop and away, across the surface, both supporting the droplet and pulling it out wider and thinner. Tiny inconsistencies lead to the formation of of the dendrites, as the area between two arms becomes saturated they are pulled apart (and closer to other arms) leading to the rapid back and forth wiggling. This continues at all scales forming similar shapes on the scale of several mm down to fractions of a mm.
It took me weeks of messing around with the camera and reading about fluid dynamics to figure this out. I even spoke with a couple of fluid dynamics experts who both told me “hey, that’s really weird, why does it do that?”
For a more detailed view I have a video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=npkv8gspVO0
Fractals are our overlords.
It looks like it forms into a fractal pattern that maximises the edge area in contact with the water and allows it to dissolve at the highest possible rate. Really cool slo-mo!
Thank you science guy!
NP, it drove me nuts to see a simple thing act in a not-simple way and just had to know.
This looks like something that’d be really fun to write a simulation shader for
Its random little mysterious things like this that can lead to breakthroughs in science. Kudos for following through and figuring out the why behind this really beautiful phenomenon.